Outlook
趨勢展望
ECOVE Implements Circular Economy by Recycling and Reusing Waste Solvents for High-tech Industries
As the world increasingly focuses on sustainability and zero waste, the global economy not only calls for reuse of resources, but also improvement in production processes, reduction of toxic or environment-adverse raw materials, or adopting longer-lasting materials, so that resource cycling can become more efficient and effective. Each year, large amount of waste solvents are generated from the semiconductor production processes in Taiwan. Based on the idea of “Every Resource Counts,” the resource cycling company ECOVE has set up a subsidiary company— ECOVE Solvent Recycling Corporation (ECOVE SRC)— to provide waste solvent treatment services for reuse. So far, ECOVE SRC has successfully helped clients concentrate and purify waste isopropanol (W-IPA) generated during the semiconductor production processes to industrial grade, sufficient to be reused for industrial purposes. This effectively lowers the depletion of the Earth’s resources. In order to utilize purified IPA more effectively, we continue to use integrative green technologies and advance our processes. The result is a high-value W-IPA recycling and reuse technology that combines membrane separation technology with the existing foundation of the distillation separation and the azeotropic distillation technologies. Such combination of technologies allows purification and separation of waste solvents, thereby improves resource utilization, increases waste value, and prolongs product life cycle, bringing more economic value to products. This article will talk about the membrane separation technology used in waste IPA treatment.

ECOVE Solvent Recycling Corporation, a subsidiary of ECOVE, recycles and reuses waste solvents.
Improve IPA Quality with Membrane Separation Technology
We assessed various industry practices used to increase the concentration of IPA for recycling and reuse. In the end, we chose a type of membrane separation technology (see Pic. ) that does not require adding other chemicals, and adopted vapor permeation (VP) method of this technology to remove the moisture content of concentrated IPA to improve product quality. The idea behind membrane separation technology is that when a membrane, which acts as semi-permeable or selectively permeable barrier, is combined with an appropriate driving force, it can enable some molecules or ions to pass through the barrier and block other molecules or ions to achieve separation. This technology surpasses traditional separation technology in that it can separate azeotropes, separate mixtures with similar boiling points, or separate heat sensitive mixtures. In addition, it saves energy, does not occupy large space, is user-friendly, and is easy to maintain. Its modular design and setup are not complicated (see Pic. 2). It also has the advantage of being able to be combined with traditional separation equipment for extension.
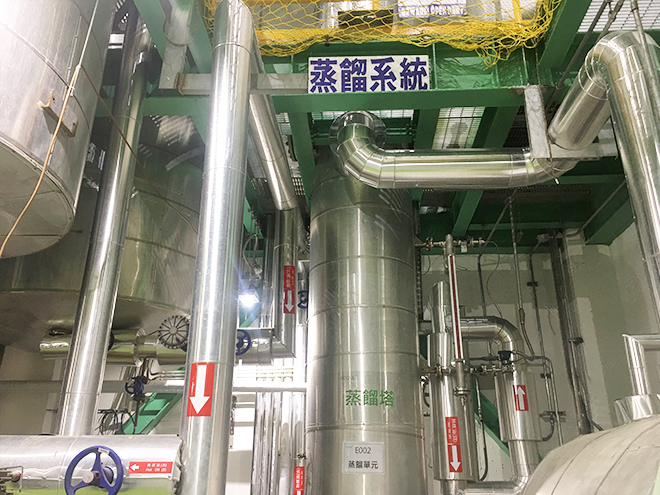
Pic. 1 ECOVE's main process for waste solvent reuse adopts membrane separation technology.


The VP method— one of the effective technologies used to separate mixed vapor— takes advantage of the different solubility and diffusion rate of the mixed vapor through the membrane to achieve separation. This type of technological application is regarded as clean technology because it does not require the addition of a third substance and is mostly used in removing water from organic solvents. It can reduce the chances of product contamination, eliminate the cost of adding the third substance, and avoid environmental pollution. There are two types of vapor permeable membrane materials: organic and inorganic. Organic membrane materials usually refer to polymer membranes. These membranes do not require sophisticated equipment to produce and process. Other benefits include diverse structure and wide range of applications. Common polymer membranes include chitosan, polyvinyl alcohol (PVA), polyacrylonitrile, polyester, cellulose acetate, and polysulfone. The drawback of this kind of membrane is that it is intolerant to high temperatures and high pressures, which narrows its practicality in some industrial procedures. Inorganic membrane materials, on the other hand, include ceramic membrane, metal membrane, molecular sieve membrane, and among others. Although they are more complicated and costly to manufacture, they enjoy far better membrane material stability, temperature tolerance, flux, and service life than organic ones (see Table 1). This is why we choose to use inorganic membrane VP technology to increase the reuse value of IPA products through green technology.
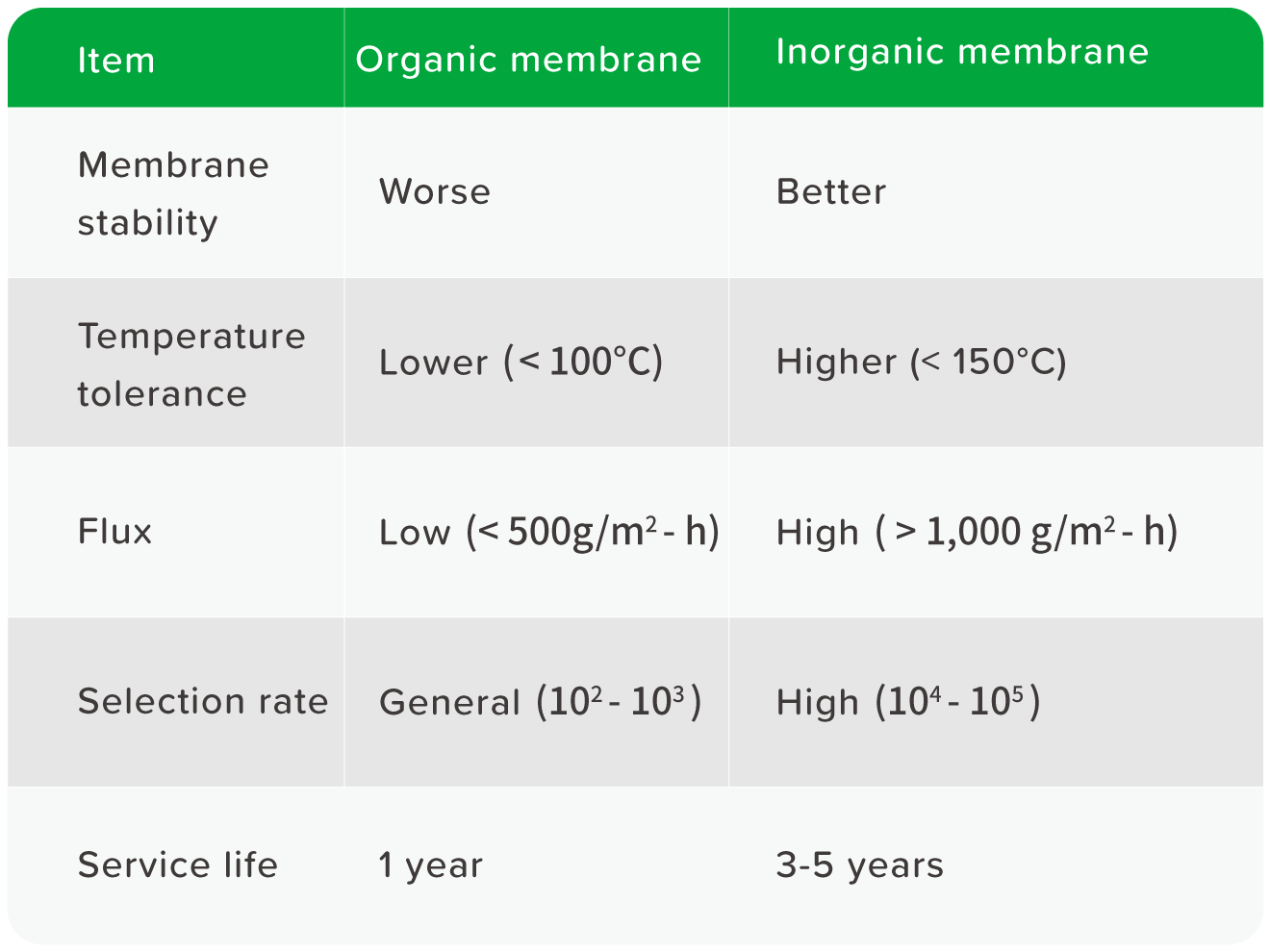
Table 1 Comparison of Organic and Inorganic Membrane Materials (Source: ECOVE)
Committed to implementing circular economy and striving towards sustainability
Converting waste into resources is the most important principle of circular economy. President Tsai Ing-wen even once called upon the nation to “head towards the era of circular economy and convert waste into renewable resources,” so that Taiwan can become aligned with international standards and create a win-win situation for the economy and environmental protection. Based on the concept of "every resource counts," ECOVE has integrated technologies and applications to help the electronics industry recycle IPA waste liquid and turn it into products by using purification technologies. This allows waste IPA to go back to the raw material market and maximize its surplus value. It also integrates upstream and downstream, and helps reduce consuming the Earth’s resources. In addition to process advancement, it is worthy to mention ECOVE SRC’s other green production efforts. One effort is to replace boiler heavy oil for the recycling process with natural gas— which is a form of clean energy. Another effort is aiming to buy green power. From process to operation, ECOVE’s operations are striving to be in line with circular economy principles. The impending climate crisis has driven more countries and regions to announce their own carbon neutrality targets. Policies, business models, energy transition, and environmental regulations have been, and will continue to be, adjusted to meet such targets. ECOVE aims to become the world's "most reliable provider of industry-leading ‘resource cycling’ services,” and will continue to spare no effort to provide effective waste solutions with competitive green technologies, implement circular economy with actions, and strive to become a green enterprise.

