Energy and Resource Conservation
■ Operational Headquarters
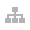
The main sources of carbon emissions from ECOVE's operational headquarters are office electricity consumption and fuel consumption of official vehicles. The headquarters office building is a Diamond-class intelligent building. Carbon reduction is carried out through energy-saving promotion, adjusting the air-conditioning temperature of the computer room, reducing the amount of lighting in ineffective lighting areas, and adjusting the intelligent energy-saving time slots. With 2022 as the base year for carbon emissions from the operating headquarters, the plan is to achieve net-zero carbon emissions from the headquarters by 2030, with a short-term target of a 20% reduction in Scope 1 and Scope 2 carbon emissions by 2024, and a mid-term target of a 40% reduction by 2026. In 2024, the total electricity consumption of the headquarters building is approximately 261,300 kWh, with an Energy Use Intensity (EUI) of 107.25 kWh per square meter and an emission intensity of 0.867 metric tons of CO2e per person. The increase in electricity consumption is attributed to the aging of data storage equipment and a significant volume of data processing, which has led to higher energy usage. By late 2024, energy efficient equipment has been gradually replaced, and by the end of 2024, electricity consumption has returned to previous levels. The primary reason for the reduction in per capita carbon emissions compared to 2022 is the use of green electricity. Currently, ECOVE's company vehicles have fully adopted hybrid vehicles, and there are plans to gradually replace them with electric vehicles to reduce carbon emissions and pollution. In 2024, 63,000 kWh of green electricity was utilized, achieving a 20% reduction in overall greenhouse gas emissions compared to the base year (with an actual reduction of 20.5%). It is anticipated that by 2026, the use of green electricity will be increased to 40% of total electricity consumption, and by 2030, the headquarters will fully utilize green electricity. In addition, ECOVE also responds to the government's green office initiatives by implementing five major indicators and 35 measures, including energy resource conservation, waste reduction at the source, green procurement, environmental greening, and advocacy and promotion. ECOVE has adopted 30 of these measures, demonstrating its commitment to making a positive impact on the environment.
■ Waste collection and transportation
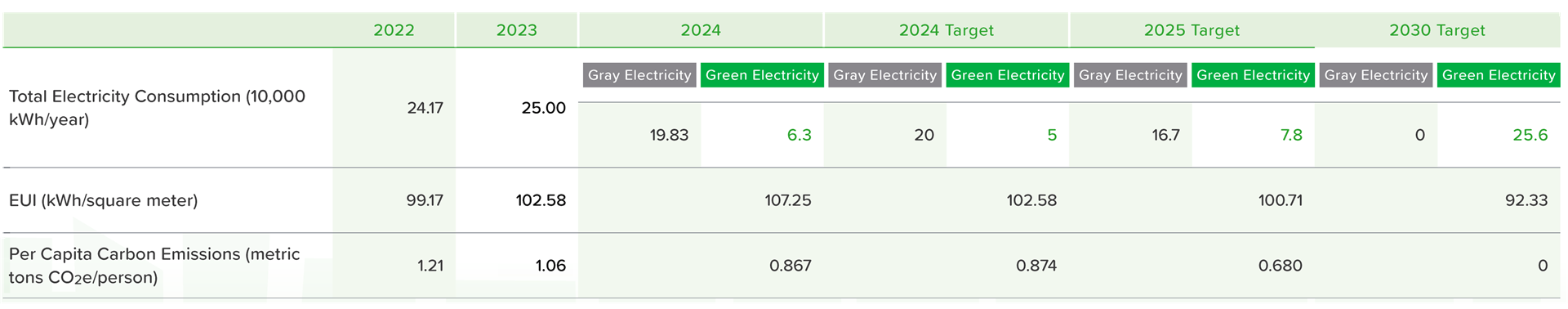
ECOVE Waste Management Corp. focuses on waste transportation and management, optimizing transportation routes and introducing environmentally friendly vehicles to reduce fuel consumption and carbon emissions. In 2024, the average fuel consumption reached 150.7 kiloliters per 500,000 kilometers, a decrease of approximately 10% compared to the base year of 2022. The carbon dioxide emission intensity (total carbon emissions in Scope 1 and Scope 2) was 403.471 metric tons CO2e, a decrease of approximately 11.3%. To further reduce carbon emissions, ECOVE Waste Management Corp. has established short-, medium-, and long-term carbon reduction plans, using 2022 as the base year. The targets are to reduce emission intensity by 15% by 2026, by 30% by 2030, and to achieve net-zero emissions by 2050. In the short term, the waste collection vehicles will be replaced with the latest environmentally friendly models, and the garbage compaction vehicles will gradually be converted to hybrid power, with an expected reduction in fuel consumption of over 20% per vehicle. Furthermore, by optimizing delivery routes and implementing a paperless dispatch system, we can further reduce pollution and resource consumption. Since 2022, the primary vehicles used for waste collection have been Stage 6 vehicles. By the end of 2024, the proportion of Stage 5 vehicles or higher has reached 89.6%, continuously enhancing the environmental efficiency of waste collection operations.
■ Waste incineration
ECOVE actively introduces the green technologies of the Group to continuously improve energy efficiency and resource conservation in its operational energy from waste plants. In 2024, a total of 26 energy/resource-saving initiatives were implemented, including the replacement of energy-saving lamps for the plant's interior lighting, the installation of inverters for large-scale wind turbines, the replacement of air condenser fans with FRP material, the renewal of chilled-water machines and improvement of furnace beds, the application of heat pumps, and the conversion of soot blowers to vibration wave ash cleaning, among other things. As a result of these energy-saving measures, a total of 5,953 metric tons of carbon dioxide equivalent were reduced in 2024.

■ Recycling
ECOVE Solvent Recycling Corp. continues to promote energysaving and carbon reduction measures. In 2024, the cooling water tower was updated, resulting in a reduction of 4.1 tons of carbon emissions annually. Additionally, variable frequency drives were installed to further decrease energy consumption, leading to an additional annual reduction of 3.9 tons of carbon emissions. In addition, the electric boiler has been replaced with a once-through boiler in the third quarter, enhancing energy utilization efficiency. Using 2022 as the base year, the carbon emission intensity of ECOVE Solvent Recycling Corp.'s unit revenue is 12.07 kilograms of CO2e per thousand New Taiwan Dollars, and a carbon reduction target has been established: In 2024, the proportion of green electricity usage reached 8.8%. In the short term, we will continue to reduce carbon intensity through process optimization while enhancing energy efficiency to achieve sustainable development goals.
Water Consumption
■ Operational Headquarters
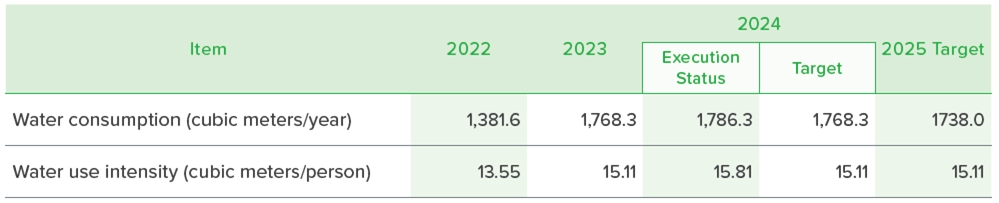
ECOVE's headquarters building relies 100% on tap water as its water source and does not draw water from any other bodies of water. All wastewater is discharged into the sewage system. In addition to extensively using automatic sensor faucets to reduce water consumption, ECOVE also controls the water flow and timing to conserve water. They have also created various water-saving slogans to remind employees to save water at all times. Rainwater harvesting systems have been installed on the rooftop of the building and at construction sites to collect rainwater for irrigation of plants or for use during construction activities. The total water consumption in 2024 was 1,786.3 cubic meters. The water use intensity was 15.807 cubic meters per person. The primary reason for the increase in water consumption is the heightened usage of the training center on the eighth floor, which has led to a slight rise in per-unit water usage. Efforts to promote water conservation will be strengthened.
■ Waste incineration
All 9 large-scale energy-from-waste plants and 2 small-scale incineration plants operated by ECOVE Environment Service Corp., a subsidiary of ECOVE, source 100% of their water from the municipal water supply. This water is primarily used for the production of boiler feedwater or the generation of soft water for process purposes. Various types of wastewaters, including process wastewater, vehicle washing wastewater, and employee domestic wastewater, are collected and treated in the on-site wastewater treatment system to meet design standards. After treatment, the water is introduced into an internal recycling system, such as for waste gas cooling, to achieve the goal of water usage reduction. By switching to a dry acid removal system at the Taoyuan and Gangshan plants after the renovation and improvement, it is expected to contribute 0.04 metric tons of water per ton of waste, thus achieving the goal of water conservation.
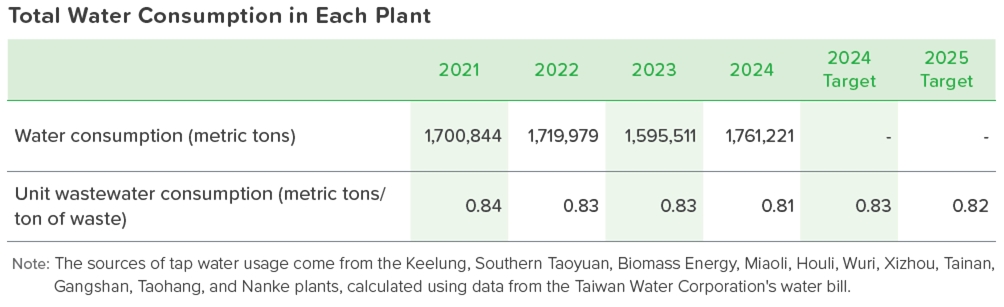

Starting from 2022, Southern Taoyuan Plant has implemented a pilot project for fly ash water-washing service. The water source for cleaning is tap water, and each ton of fly ash requires 3 tons of water. After treatment, the waste water meets the discharge standards of the Zhongli Industrial Park and is discharged into the industrial park's sewer system.
■ Recycling
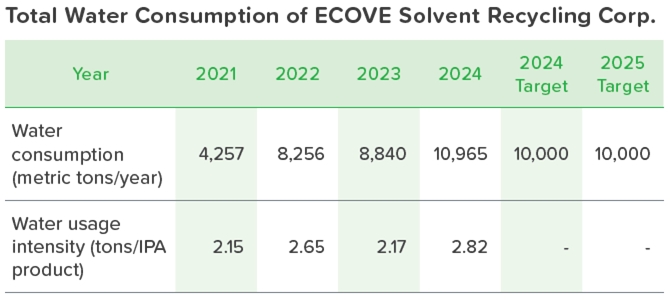
ECOVE Solvent Recycling Corp.'s operational water is primarily used for cooling systems, and the water source is 100% from the public water supply. Therefore, there are no significant impacts on water sources.
Waste
■ Operational Headquarters
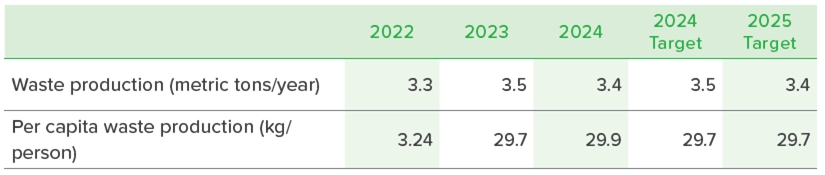
The general waste disposal method for the headquarters building is incineration, which generated 3.38 metric tons in 2024. Recycling management is implemented for paper, metal, plastic, and food waste. Through recycling management, reduction of general waste is made possible. In 2024, the management of recycling for paper containers (including lunch boxes, beverage cups, etc.) was further enhanced.
■ Waste incineration
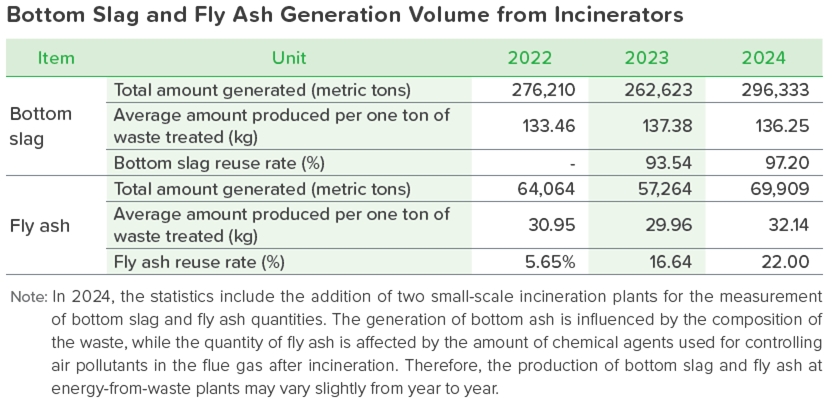
In 2024, the 9 large-scale energy-from-waste plants and 2 small-scale incineration plants operated and managed by ECOVE ESC generated 296,333 metric tons of bottom slag, or an average of 136.25 kilograms of bottom slag per ton of waste treated; and 69,909 metric tons of fly ash, or an average of 32.14 kilograms of fly ash per ton of waste treated. The bottom slag is sampled and tested in accordance with the regulations to confirm compliance with the bottom slag reuse management method, and then transported to the bottom slag reuse site or temporary storage plant, with an average reuse rate of 97.20% in 2024; the fly ash is stabilized and then packaged in bags, or sent to the melting and reuse and washing for reuse, and the stabilized material is sampled and tested before being sent to qualified landfill sites for sanitary landfill, so that no methane fugitive emissions will occur during the landfill process. A total of 15,381 metric tons of fly ash was sent for reuse in 2024, increasing the reuse rate from 5.65% in 2022 to 22.00%. The Gangshan Plant has installed a bottom slag sorting system to recover and reuse the metals in the bottom slag to further reduce the amount of bottom slag, and the Southern Taoyuan and Gangshan Plants have begun to adopt a new dry deacidification system, so that fly ash production can be further reduced. Taiwan's current large-scale energy-from-waste plants7 do not receive hazardous waste, and the bottom slag and fly ash stabilizers are considered to be general utility waste according to the hazardous waste identification standards. Each plant is required by law and contract to test the frequency of compliance with the standards before final landfill disposal, and legal landfills must be equipped with an impermeable layer to isolate the natural body of water and an independent wastewater collection and treatment system, and there has not been any need to assist in the improvement of the landfill for substances released. 7 A waste incineration plant that has a designed daily processing capacity of over 300 metric tons and is owned, managed, or supervised by the municipal or county (city) competent authority or executing agency.
■ Recycling
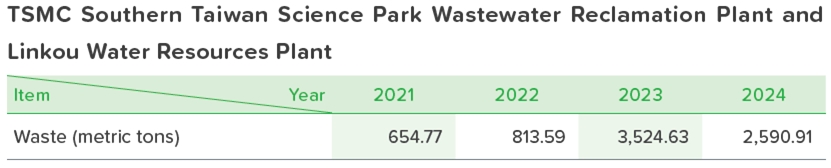
The main source of waste from the wastewater treatment plant is sludge, and the amount of waste in the last four years is shown in the table below:
■ Solar Photovoltaics
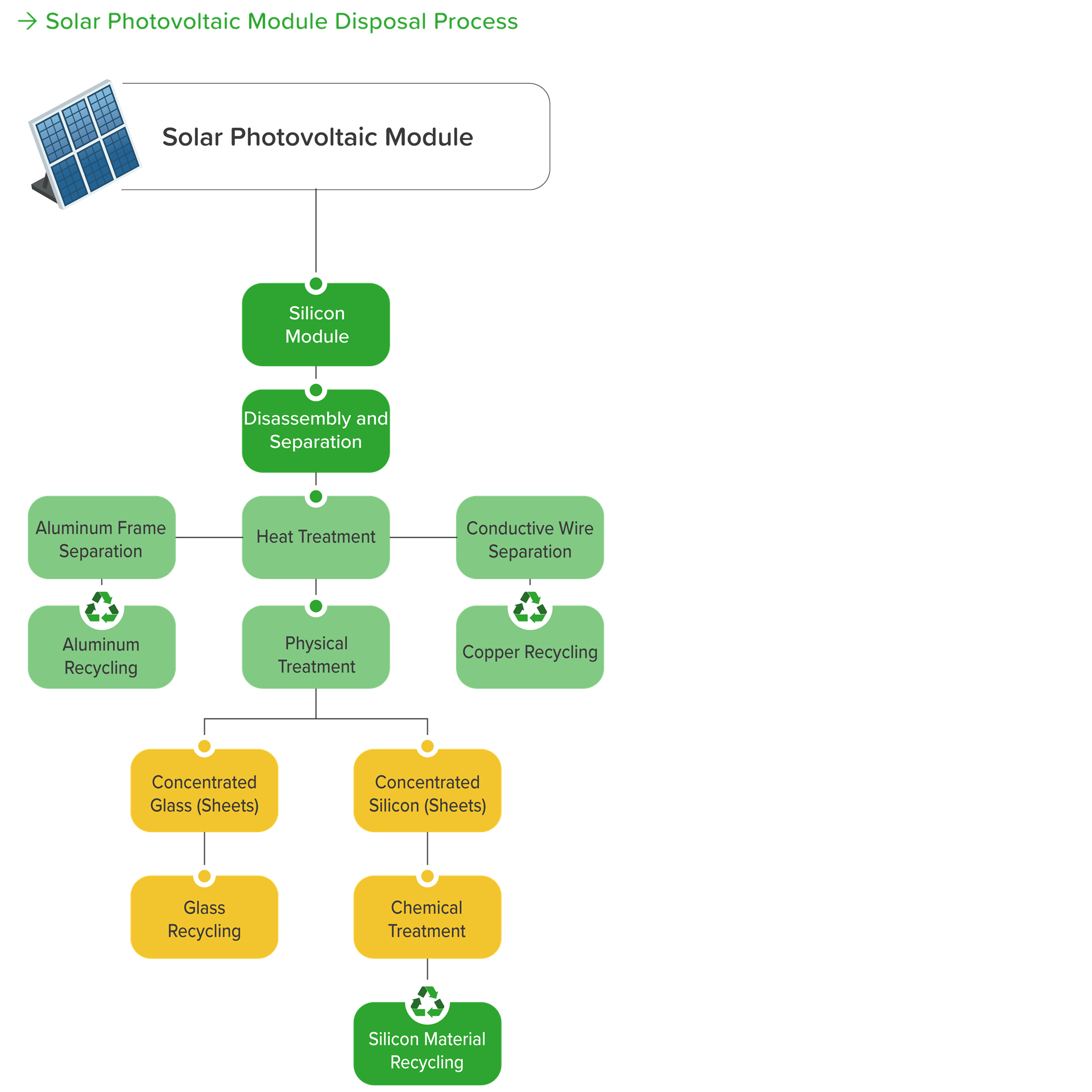
Solar panels mainly consist of modules, brackets, inverters, junction boxes, cables, and other electrical equipment. According to the "Regulations on the Installation and Management of Renewable Energy Power Generation Equipment," Article 17 states that solar panel installers are required to pay module recycling fees. These fees are collected by the Ministry of Environment to establish a module recycling mechanism for proper management of retired photovoltaic modules. ECOVE complies with the relevant regulations regarding the disposal of retired photovoltaic modules. The current disposal method involves centralized storage of retired solar panels and registering their serial numbers for module material tracking. When the recycling quantity specified by the Ministry of Environment is reached, waste solar panel transportation companies are commissioned to handle the disposal in accordance with regulations, ensuring that the recycling of discarded modules is compliant and environmentally friendly.
Pollution Control
■ Waste incineration
In order to effectively control the emission of air pollutants, ECOVE Environment Service Corp. has set up a continuous emission monitoring system (CEMS) to monitor seven items, including exhaust gas flow rate, oxygen content, sulfur oxides (SOx), nitrogen oxides (NOx), hydrogen chloride (HCl), carbon monoxide (CO), and opacity, which are continuously monitored 24 hours a day and uploaded real-time to the website of the Ministry of Environment8 to ensure transparency. Currently, the monitoring data of the 9 large energy-from-waste plants and two small-scale incineration plants operated by ECOVE Environment Service Corp. can queried through an online system. In addition, regular on-site inspections are conducted on a monthly or quarterly basis to assess various parameters including sulfur oxides, nitrogen oxides, particulate matter, heavy metals, and dioxins to ensure that emissions comply with environmental regulations. The Ministry of Environment imposes air pollution fees on fixed sources of pollution, including sulfur oxides, nitrogen oxides, volatile organic compounds (VOCs), particulate matter, heavy metals, and dioxins. Among these, nitrogen oxides (NOx) have higher emission levels and are classified as key performance indicators (KPIs) for management. Taking 2022 as the base year, the nitrogen oxide emission intensity of ECOVE Environment Service Corp. was 0.93 kilograms per metric ton of waste. Through enhanced pollution control measures, this intensity has further decreased to 0.81 kilograms per metric ton of waste in 2024, thereby continuously improving air quality and fulfilling environmental sustainability objectives.
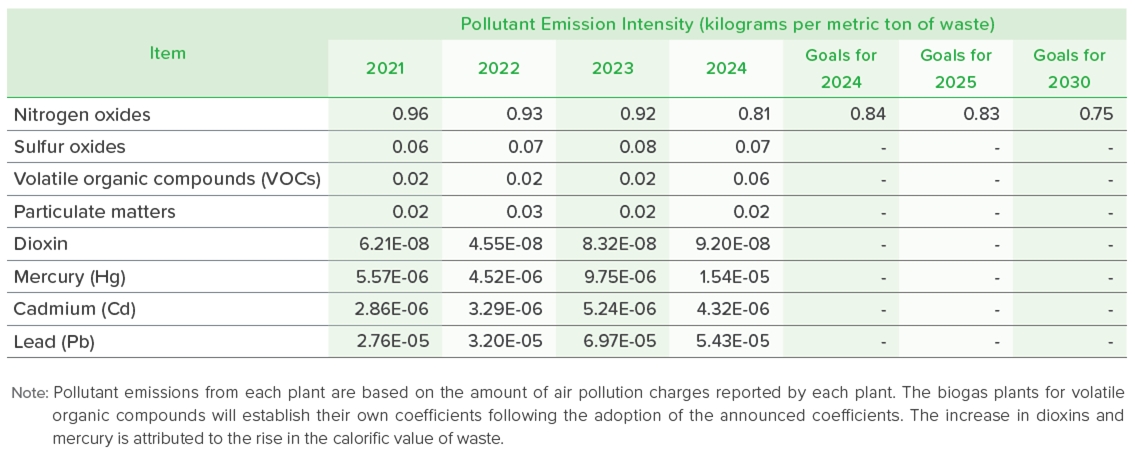
■ Recycling
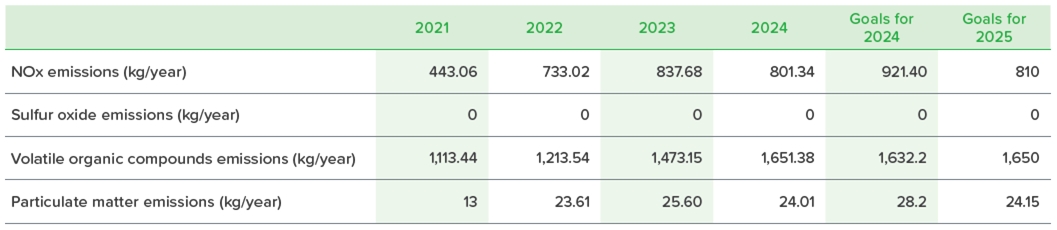
ECOVE SRC has also introduced an environmental management system (ISO 14001) to regularly monitor the emission pipeline, and changed the fuel used for the original boiler from heavy oil to natural gas to reduce the emission of air pollutants; however, due to the increase in the amount of recycling volume year by year, the amount of natural gas used has also increased.
Wastewater treatment/waste water reclamation plant laboratory provides accurate water quality data, but it requires a longer analysis time, making it difficult to reflect changes in water quality in real-time. To improve real-time monitoring capability, the plant is equipped with an automatic continuous monitoring system. This system utilizes automated analyzers to provide rapid but less precise water quality data; however, it makes real-time data of discharged water quality trends readily available and enables operational units to quickly respond and adapt to the trends in discharged water quality. It also serves as a reference for regulatory authorities and the general public. Through water quality analysis and automated continuous monitoring, in 2024, 100% of the wastewater discharges from all wastewater plants complied with the standards for discharges or industrial zones, ensuring that water quality complies with regulatory requirements and maintaining environmental safety.
■ Achievement of Water Quality Standards for Discharged Water from Various Water Treatment Plants
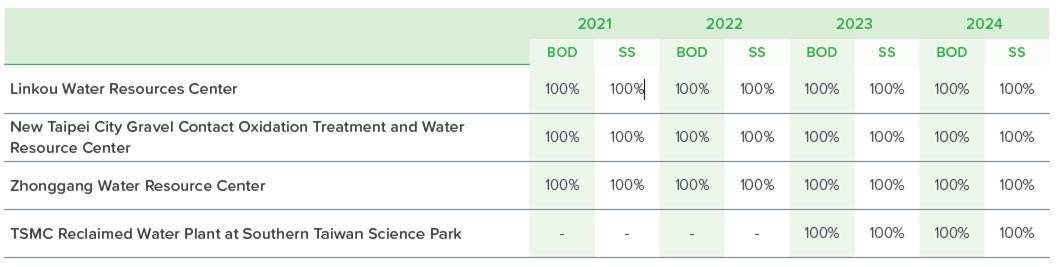

Water quality analysis