Biodiversity Commitment
The stability of the human living environment is significantly influenced by biodiversity, and the maintenance of biodiversity is key to achieving sustainable development. Whether it is the raw materials required for business operations or the necessities of daily life such as food, clothing, housing, and transportation, all rely on natural resources. However, with the accelerated development of society, natural resources are being rapidly consumed, which impacts the balance of ecosystems. ECOVE recognizes the importance of biodiversity for climate stability and sustainable development. Therefore, we have formulated the "Biodiversity and Zero Logging Policy Commitment" to demonstrate our responsibility towards ecological conservation. By collaborating with upstream and downstream partners and stakeholders, we will expand our influence and commit to creating a stable and healthy ecological environment, contributing to sustainability for future generations. We commit to and implement the following actions:





Ecological and Environment Protection Strategies and Planning
The Environmental Protection Unit under the Sustainable Development Committee of ECOVE is responsible for the strategic planning and implementation of the nature and biodiversity strategy, covering the headquarters building and all operational sites in Taiwan. Establish short-term, medium-term, and long-term goals for biodiversity conservation. The medium-term goal is to achieve No Net Loss (NNL) and Zero Deforestation in its operation sites by 2030. The long-term goal is to achieve Net Positive Impact (NPI) and No Net Loss and Zero Deforestation in its value chain in its operation sites by 2050.
Ecological Environment Protection Target Planning
- 2023
- Suggest avoidance and mitigation measures
- Reduce the impact of unavoidable shocks by taking restoration measures
- Compensate for unrecoverable impacts (e.g., restoration of the environment)
- 2025
- Completion of the inclusion of biodiversity and zero-deforestation related policies in the Code of Conduct
- 2030
- Achievement of NNL for biodiversity at operation sites
- Zero-deforestation monitoring at the operation sites
- 2050
- Achievement of NPI at operation sites
- NNL in value chain
- Compliance with Zero Deforestation Standards in value chain
Note 1: NNL is a zero change in total ecosystem species at the point of operation using restoration. Note 2: NPI is the amount of change in the total number of organisms in the operation that is positive by means of restoration and compensation.

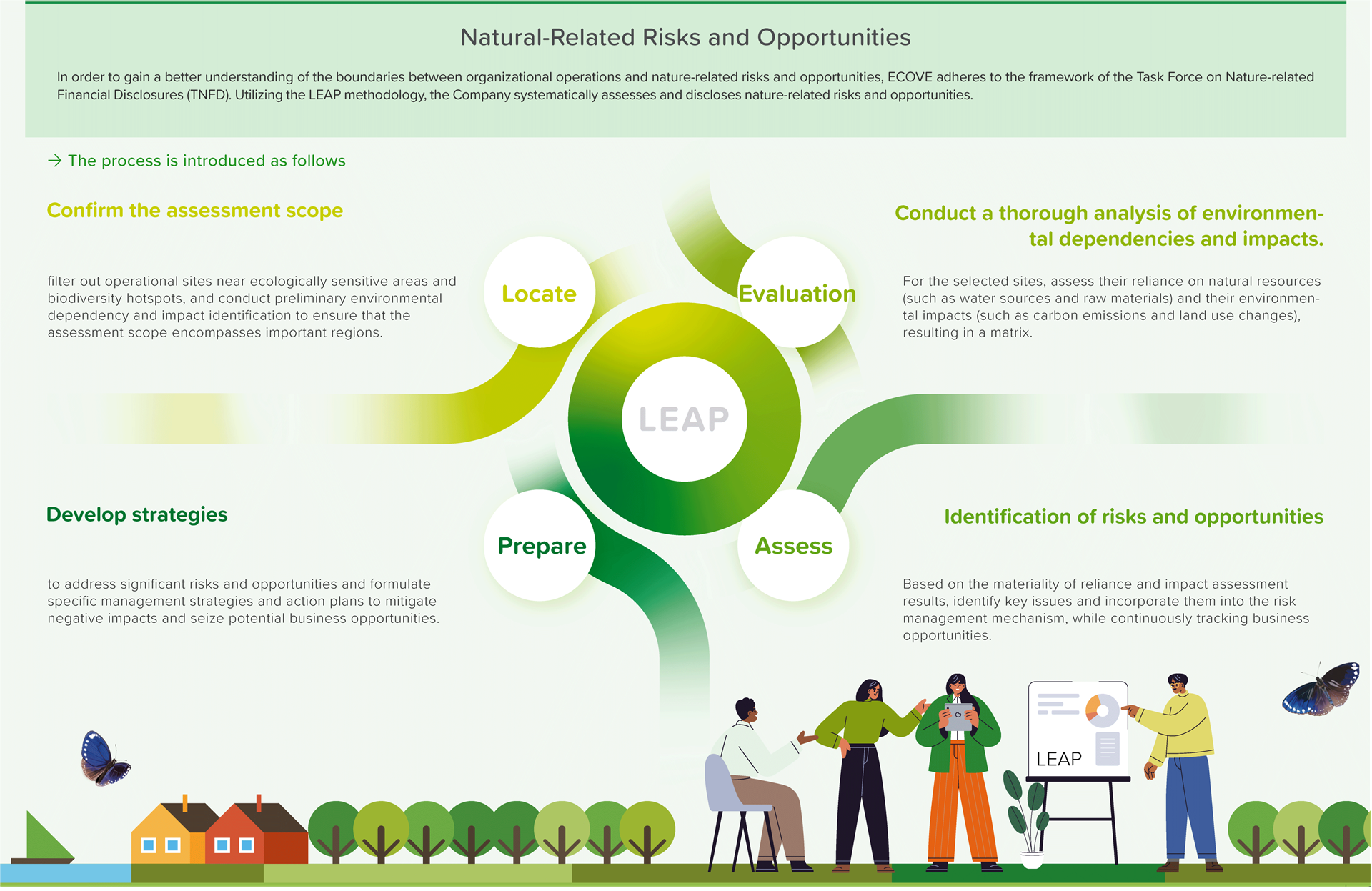
Natural-Related Risks and Opportunities
In order to gain a better understanding of the boundaries between organizational operations and nature-related risks and opportunities, ECOVE adheres to the framework of the Task Force on Nature-related Financial Disclosures (TNFD). Utilizing the LEAP methodology, the Company systematically assesses and discloses nature-related risks and opportunities.
Analysis of Ecologically Sensitive Areas and Hot Spots
To comprehensively understand the ecological environment surrounding operational sites and to confirm the interactions between the Company's business activities and the ecosystem, thereby facilitating effective ecological conservation and sustainable management, ECOVE utilizes the Taiwan Biodiversity Network (TBN) from the Council of Agriculture, Executive Yuan, as well as the World Database on Protected Areas (WDPA) to identify biologically sensitive areas and biodiversity hotspots across all operational sites. The identification results are as follows: Keelung Incineration Plant is partly located in a biodiversity hotspot, while Miaoli Incineration Plant and Tainan Incineration Plant are adjacent to ecologically sensitive areas and are also situated within a biodiversity conservation corridor.
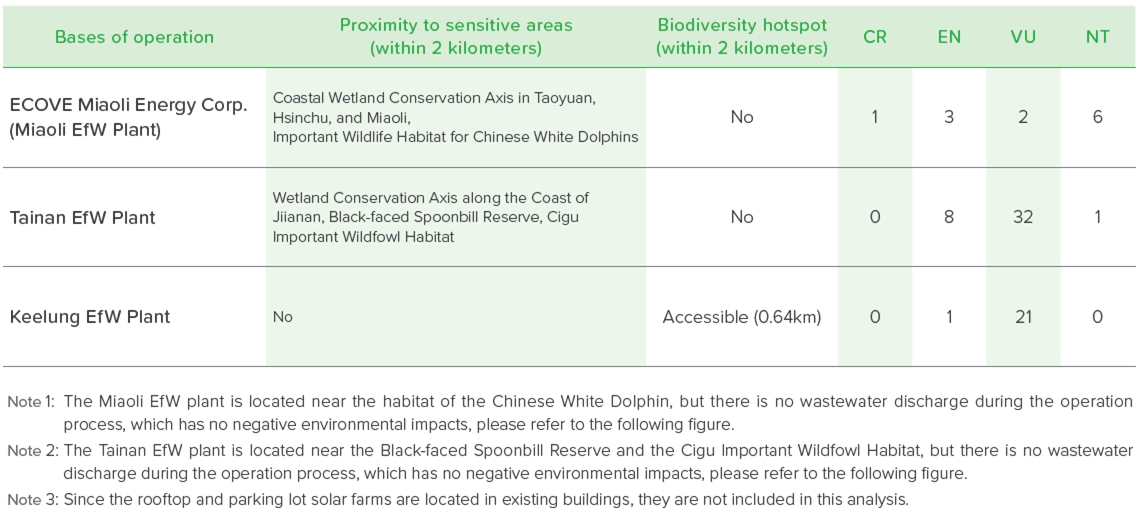
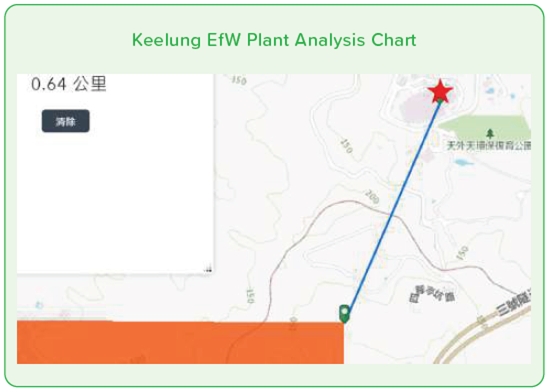
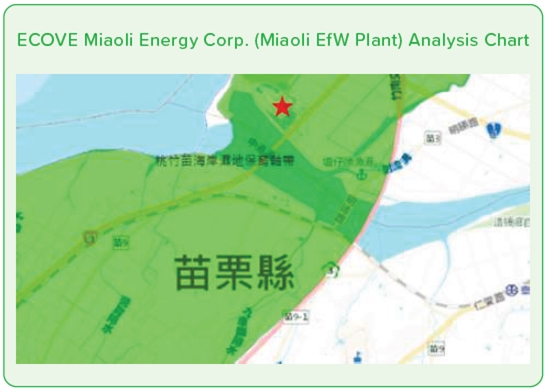
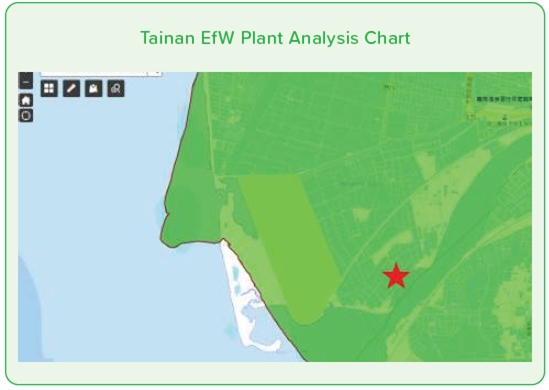
Note: 1. The red star indicates the location of the plant. Note: 2. The orange area represents the biodiversity hotspot. Note: 3. The green area represents the ecologically sensitive zone.
Analysis of the Natural Ecosystem Dependency of Operational Locations
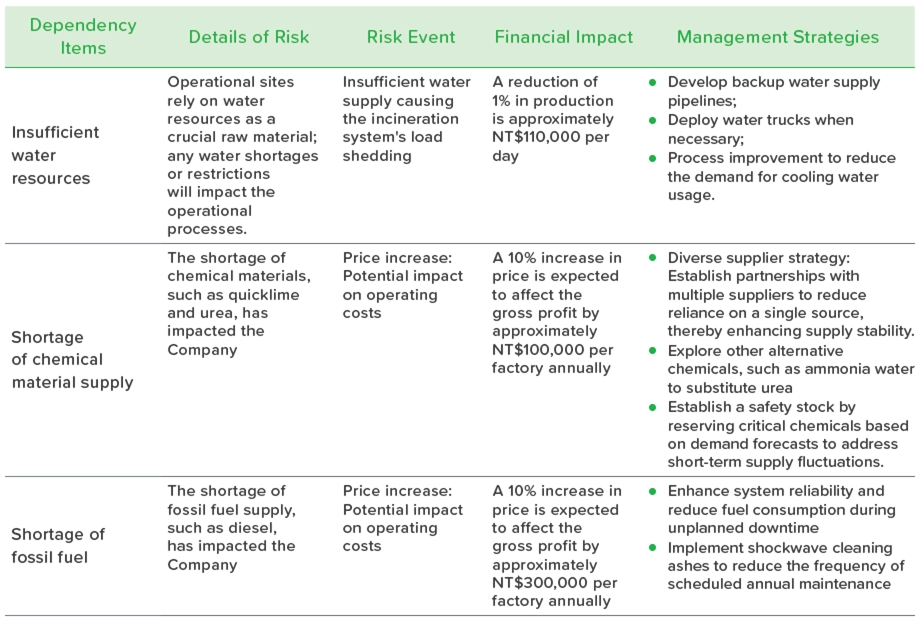
This risk identification operation is based on a survey form as the primary tool, combined with in-depth interviews and discussions with colleagues from the operational units, ultimately resulting in the formation of a risk issue matrix for systematic analysis. This method aids in comprehensively understanding the risk issues that require heightened attention during operations. The analysis results indicate a high-exposure issue—water resource scarcity—that may have a direct impact on operational efficiency and the work environment for employees. Additionally, two potential high-risk issues have been identified: "shortage of fossil fuel supply" and "shortage of chemical material supply," which pose potential challenges to supply chain stability and production continuity. In response to the aforementioned risks, we return to the operational level to establish a risk management mechanism, which includes continuous monitoring, contingency planning, and resource allocation, in order to mitigate potential impacts. Meanwhile, we are also strengthening our risk tracking and early warning mechanisms to ensure that we can quickly adjust our operational strategies in the face of future challenges, thereby maintaining stable operations and achieving sustainable development goals.
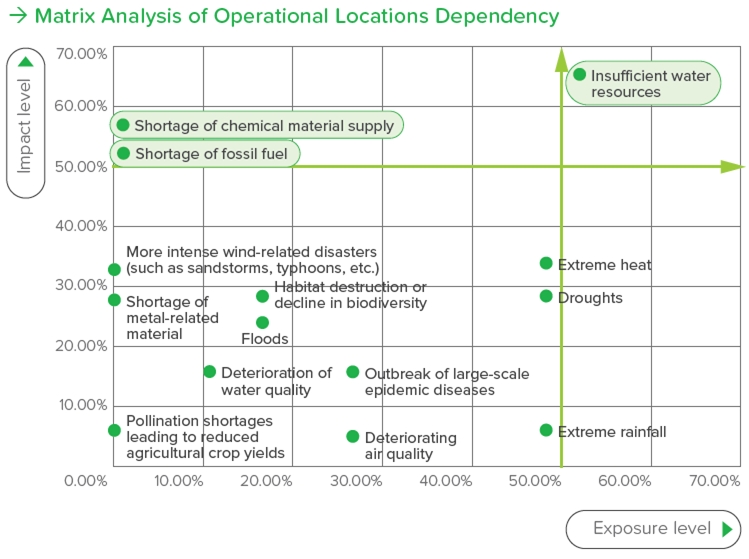
Risk Summary of Operational Locations Dependency
Opportunity Summary of Operational Locations Dependency
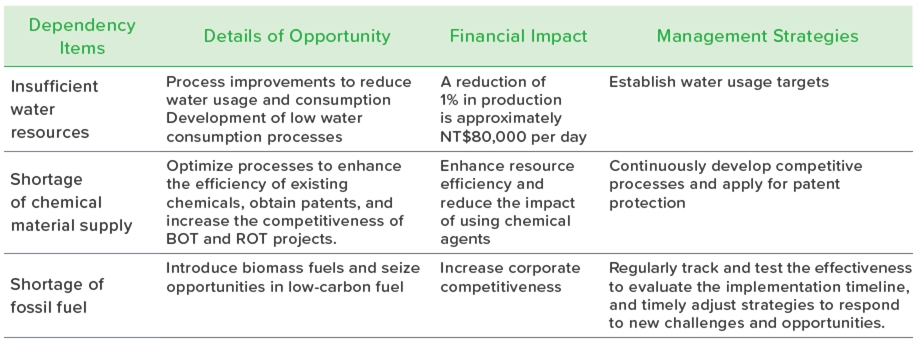
Analysis of the Natural Ecosystem Impact of Operational Locations
After identifying operational dependencies and potential risks, we conducted a systematic analysis using the same matrix to assess the potential impacts of business operations on the environment. The results indicate six high-exposure issues, including: emissions of air pollutants, water resource usage, direct use of fossil fuels, use of chemical resources, greenhouse gas emissions, and proximity to biodiversity-sensitive areas. These environmental impacts are not only related to resource availability and ecological balance but are also closely tied to the company's regulatory compliance and social responsibility. Furthermore, the use of indirect energy remains a high-risk issue even after adjustments. The carbon emissions from indirect energy and the proportion of renewable energy will directly impact the carbon footprint and carbon reduction targets during the operational process. Therefore, in response to this issue, we will continue to strengthen our energy management and low-carbon transformation strategies to reduce environmental impact while enhancing the operational resilience and sustainable competitiveness of the enterprise.
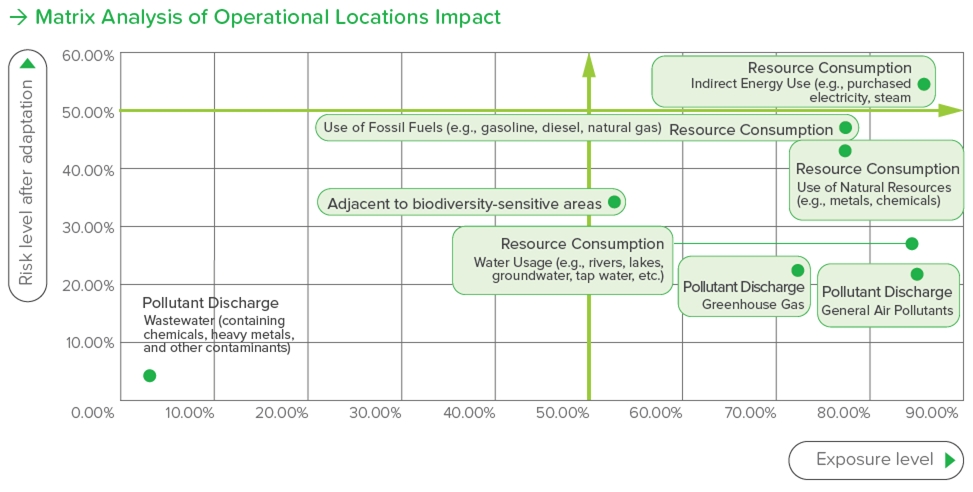
Risk Summary of Operational Locations Impact
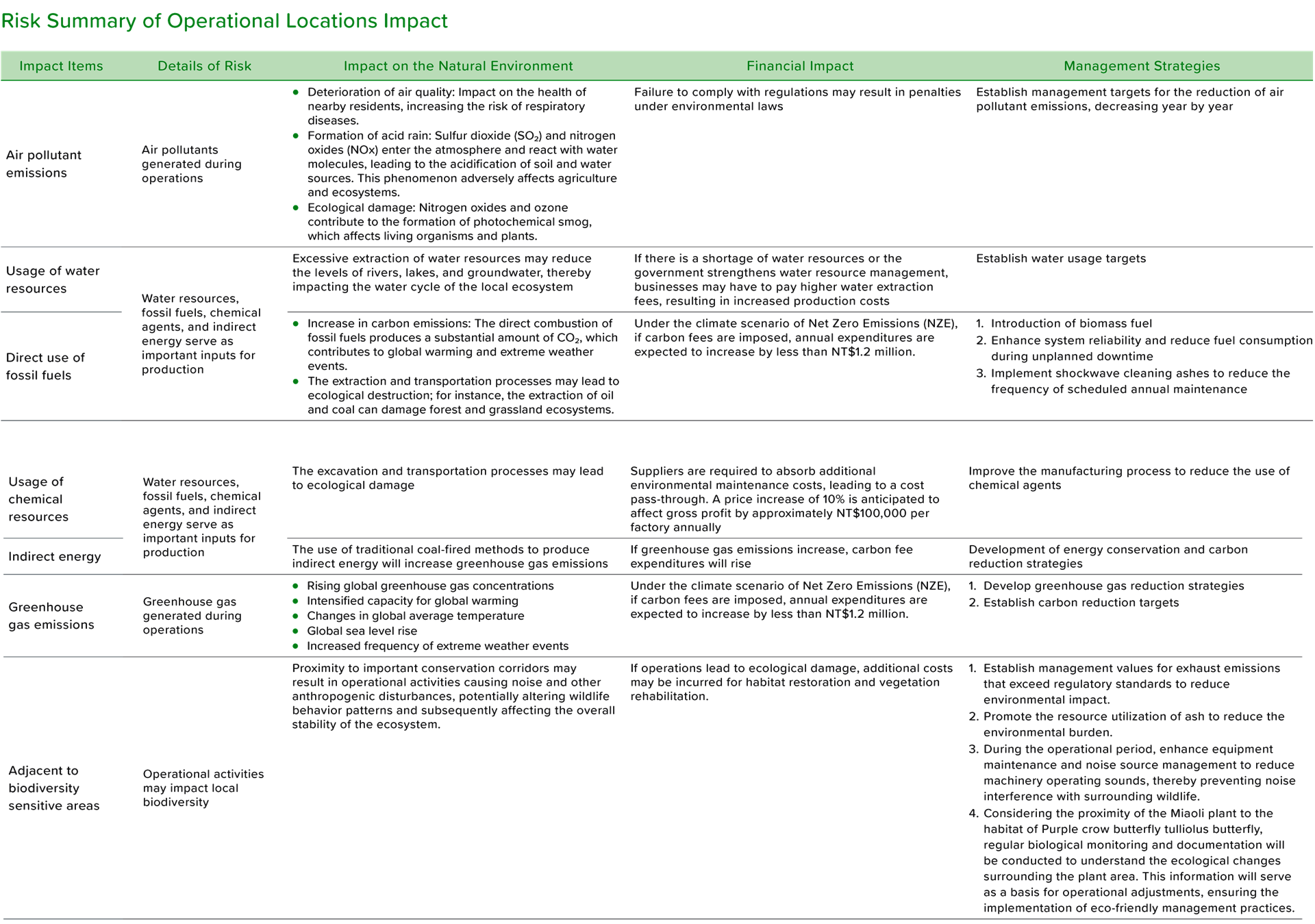
Opportunity Summary of Operational Locations Impact
Biodiversity Project I Lifelong Conservation Plan for the Purple Crow Butterfly
Protecting the Purple Crow Butterfly
◉ A Precious Asset of Biodiversity
The purple crow butterfly belongs to the family of Nymphalidae and is one of the most representative butterflies in East Asia and Southeast Asia. Its wings are deep brown or black, and due to their unique structure, they can refract light, displaying a dazzling iridescent blue and purple color. This is also the origin of the name "purple crow butterfly." However, what is most striking about the purple crow butterfly is not only its appearance but also its large-scale migratory behavior in Taiwan. Every winter, before the arrival of the season, the purple crow butterfly population migrates from northern Taiwan to the south, gathering in specific valleys or forests to escape the cold weather. This large-scale seasonal migration behavior is extremely rare and, alongside the Monarch Butterfly of Mexico, represents one of only two butterfly species in the entire world that engage in such extensive migration. This phenomenon makes the Purple Butterfly Valley in Taiwan a world-class attraction that draws global attention. Butterflies play a crucial role in the ecosystem, not only as pollinators that assist in plant reproduction but also as an important component of the food chain, influencing ecological balance. Due to their extreme sensitivity to environmental changes, butterflies are regarded as important indicators of ecological health. However, due to habitat destruction, pesticide use, and the impacts of climate change, the population of the purple crow butterfly has significantly declined in recent years, drawing attention from various sectors of society.
The Actions of ECOVE
◉ Protecting the Sustainable Future of the Purple Crow Butterfly through Actions
ECOVE is committed to ecological conservation and actively implements biodiversity management strategies. The Zhunan Wetlands adjacent to the ECOVE Miaoli EfW Plant is one of the most important breeding grounds for the Purple crow butterfly tulliolus butterfly. Additionally, several operational sites from Keelung to Chiayi coincide significantly with the migratory pathways of the purple crow butterfly. This realization deepens our awareness of our responsibilities and obligations in protecting biodiversity. In collaboration with Taiwan Purplecrow Butterfly Ecological Preservation Association, ECOVE is committed to maintaining their habitats and creating a friendly living environment for these beautiful purple fairies.

Invite the client to join us in protecting the purple crow butterflies.

The EfW plant has established a special area for environmental education on the purple crow butterfly, promoting ecological knowledge about the purple crow butterfly to the public

ECOVE has held a workshop to train colleagues to become seed teachers and ecological guides for the purple crow butterfly
Purple Crow Butterfly Conservation Plan
The promotion of the Purple Crow Butterfly Conservation Program encompasses three major aspects: habitat creation, environmental education, and the promotion of corporate culture:
◉ Establishing a habitat friendly to purple crow butterflies
Establishment of butterfly rest stations: Pilot programs for purple crow butterfly rest stations will be implemented at existing locations, providing supplies and a resting environment during their migration, thereby reducing survival pressures caused by environmental changes. Based on the butterfly periods of the purple crow butterfly in the northern, central, southern, and eastern regions, as well as the local climatic conditions, we have collaborated with the Taiwan purple crow butterfly Ecological Preservation Association to develop a reference guide for friendly planting. This guide is intended to provide companies with reference points for site selection and construction design.
◉ Promoting environmental education and knowledge dissemination
Purple crow butterfly environmental education zone: An environmental education zone for the purple crow butterfly will be established at a location near the butterfly pathway. Environmental education programs will be designed, and seed teacher workshops will be held to train staff to become guides to promote knowledge of the ecology of purple crow butterfly to the general public. ESG digital platform knowledge sharing: ECOVE has integrated environmental education materials on the purple crow butterfly and established a dedicated section for the purple crow butterfly on the corporate ESG official website, providing the latest conservation information and knowledge to expand its influence.
◉ Corporate culture and public promotion
Development of cultural and creative products: Incorporating the characteristics of the purple crow butterfly, we designed LINE stickers, commemorative coasters, eco-friendly stickers, and educational cards to enhance public awareness and understanding of the purple crow butterfly. Sustainability report and corporate image design: Integrating the imagery of the purple crow butterfly into the corporate brand, showcasing the conservation concept of the purple crow butterfly on the cover of the Sustainability Report and various promotional materials, while continuously promoting the value of biodiversity in corporate activities and promotional items.
Collaborating with the Taiwan Purple Crow Butterfly Ecological Preservation Association to enhance conservation efforts
Habitat health survey: The Zhunan Bao'an Forest adjacent to the Miaoli EfW Plant serves as the largest breeding ground for the purple crow butterfly tulliolus butterfly. The Miaoli Plant will conduct regular terrestrial plant ecological surveys to assess the health status of the habitat's vegetation and will provide the data to the Taiwan purple crow butterfly Ecological Preservation Association for reference. Training and assistance for volunteer tagging of purple crow butterflies: Actively cooperating with the Taiwan purple crow butterfly Ecological Preservation Association to implement tagging operations, utilizing scientific monitoring to understand the migration paths and population changes of the purple crow butterflies. Design and guidance of purple crow butterfly-friendly vegetation: Based on the butterfly periods of the purple crow butterfly in the northern, central, southern, and eastern regions, as well as the local climatic conditions, we have collaborated with the Taiwan purple crow butterfly Ecological Preservation Association to develop a reference guide for friendly planting. This guide is intended to provide companies with reference points for site selection and construction design.

Designing LINE stickers and commemorative coasters that incorporate the characteristics of the purple crow butterfly

Colleagues assisted in the execution of the purple crow butterfly tagging operation at Maolin

Colleagues assisted in conducting an ecological survey of the purple crow butterfly at Miaoli Plant.
Taiwan is renowned as the "kingdom of butterflies," and the purple crow butterfly is one of the most representative migratory butterflies of this land. Through the conservation efforts for the purple crow butterfly, ECOVE not only fulfills its commitment to biodiversity but also demonstrates its responsibility towards sustainable environmental development. In the future, we will continue to deepen our conservation programs by integrating engineering expertise with environmental management experience. We will collaborate with various sectors of society to jointly protect the habitat of the purple crow butterfly, allowing these beautiful purple wings to gracefully flutter for generations, witnessing the possibility of harmonious coexistence between business and nature.
Community Collaboration
"The Tainan Incineration Plant is located in the Jianan Coastal Wetland Conservation Axis, the Black-faced Spoonbill Reserve, and the Cigu Important Wildfowl Habitat, and is close to the Taijiang National Park. In order to actively participate in and support ecological conservation activities, the Tainan Incineration Plant will cooperate with the Taijiang National Park to conduct environmental education, and for two consecutive years on World Oceans Day, the plant has participated in the Land Crab Conservation in the Windbreak of Tainan Chengxi to clean up the land crab's home through teamwork to clean up trash such as floating Polaroid under the Windbreak, and to protect the home of the land crab, and to further strengthen the importance of the ecology and the environment by taking practical actions. Through such ecological conservation activities, we hope to call on all sectors of the community to work together to protect the ecological habitat, so that the living organisms can reproduce sustainably and maintain the balance of the ecosystem, as well as to promote the joint efforts for the balance of the ecosystem.

I. Equipment replacement and system upgrade
Replacement of outdated equipment, including bag-type dust collectors, Distributed Control Systems (DCS), steam turbine Programmable Logic Controllers (PLC), garbage hoist rail tracks, and hoist PLCs. The renewal of the DCS, gas turbines, and crane PLC not only ensure a reliable supply of spare parts in the future but also enhance system stability. Additionally, the renewal of the crane tracks reduces abnormal conditions and improves equipment reliability.
II. Enhancing operational efficiency
To enhance incineration efficiency, modifications were made including the lowering of the drying section grate, the replacement of high-alloy coated furnace tubes, and the replacement of the ACC fan blades with Fiber Reinforced Plastic (FRP) blades. The lowering of the furnace bed effectively reduces the slagging condition of the furnace wall. The high-alloy coated furnace tubes enhance waste heat absorption, thereby increasing steam production. Additionally, the lightweight FRP fan blades reduce the load and decrease power consumption. Additionally, the installation of variable frequency control systems for the primary and secondary air fans has replaced the fixed operation mode, resulting in a reduction of current from an average of 92A to 27A, achieving an energy savings of 70%.