Climate Change Management
Greenhouse Gas Inventory
In response to the government's net-zero carbon policy, ECOVE is conducting comprehensive greenhouse gas emission inventories. Organizational-level greenhouse gas inventories are conducted for subsidiaries with operational control, and third-party certifications are obtained. In addition, self-assessments are carried out for other operated energy-from-waste plants. Using the year 2022 as the base year, ECOVE Headquarters has set reduction targets as follows: a 20% reduction by 2024, a 40% reduction by 2026, and achieving net-zero emissions by 2030. For subsidiaries in the areas of waste management, recycling and renewable energy, which are under long-term operational control, a 15% reduction is set for 2026 and net zero for 2050.
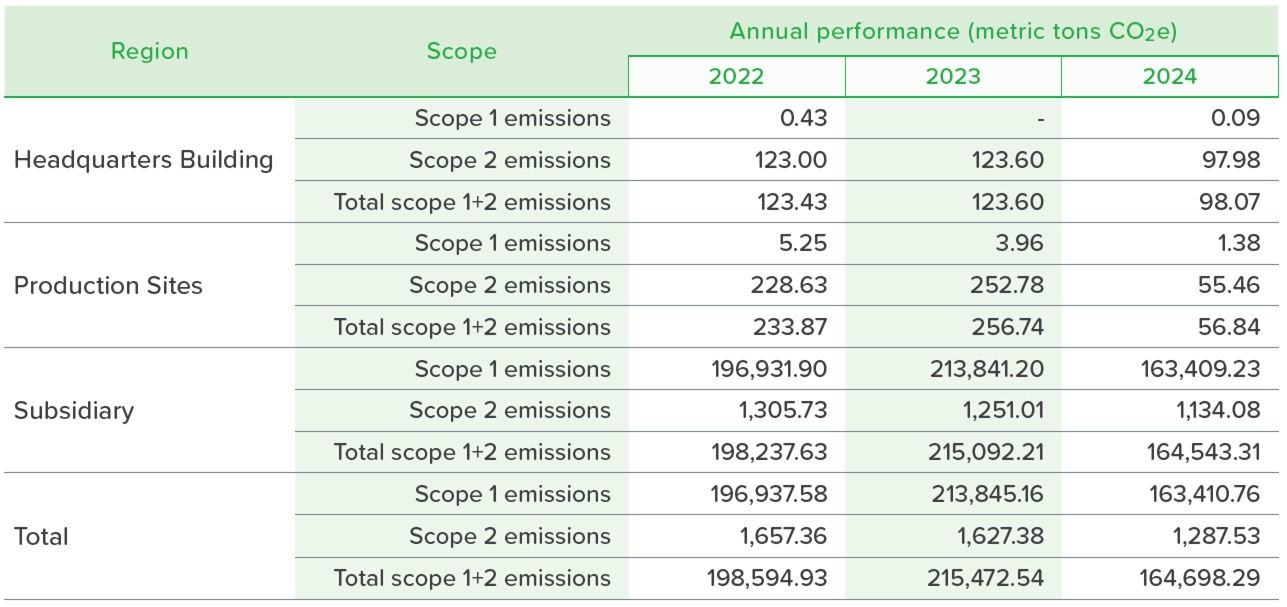
1: The biomass emissions equivalent from waste incineration is calculated based on garbage sampling analysis. 2: The emission factor data for 2024 is sourced from the announcement by the Bureau of Energy, MOEA, stating that the carbon emission factor for electricity in 2023 is 0.494 kg CO2e/kWh, with a Global Warming Potential (GWP) value based on IPCC AR6. 3: Due to the difficulty of disaggregating electricity consumption, Scope 2 emissions for ECOVE include the electricity consumption of its subsidiary headquarters as well. 4: In 2024, former subsidiaries ECOVE Solar Energy Corporation and South One Solar merged into ECOVE Environment Corporation. 5: The target for the headquarters building in 2024 is a 20% reduction in total emissions compared to the base year, with an actual reduction of approximately 20.5%. 6: The carbon dioxide emission intensity of the subsidiaries is detailed in each chapter. 7: Scope 1 emissions account for 99% of the total emissions. 8: The types of greenhouse gas inventories include carbon dioxide (CO2), methane (CH4), nitrous oxide (N2O), hydrofluorocarbons (HFCs), perfluorocarbons (PFCs), sulfur hexafluoride (SF6), and nitrogen trifluoride (NF3). 9: The biological source carbon dioxide emissions amount to 210,570.057 metric tons of CO2e per year. 10: 2022 has been established as the base year because it was the first year of the implementation of greenhouse gas inventory. 11: The method for compiling greenhouse gas emissions is the operational control method. 12: The method used is ISO 14064-1:2018.
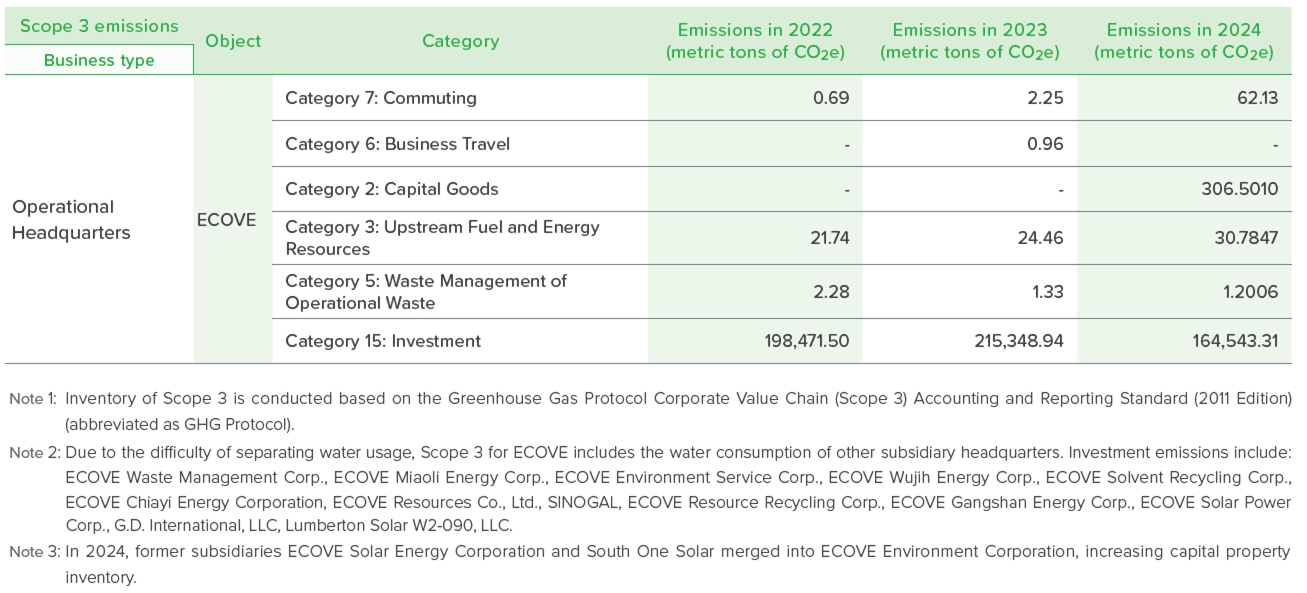
ECOVE Environment Service Corp. cooperated with the Group to conduct an organizational greenhouse gas inventory of nergy-from-waste plants managed by the Group in 2022, to determine the emissions of each emission source, and then continue to improve energy conservation and energy efficiency, and set 2022 as the base year to control the intensity of emissions. The emission intensity for 2024 is 441 kgCO2/t, representing a reduction of approximately 3.3% compared to the base year of 2022. This decrease is primarily attributed to ongoing energy conservation efforts and improvements in energy efficiency.