Practitioner of Resource Cycle and Environmental Sustainability
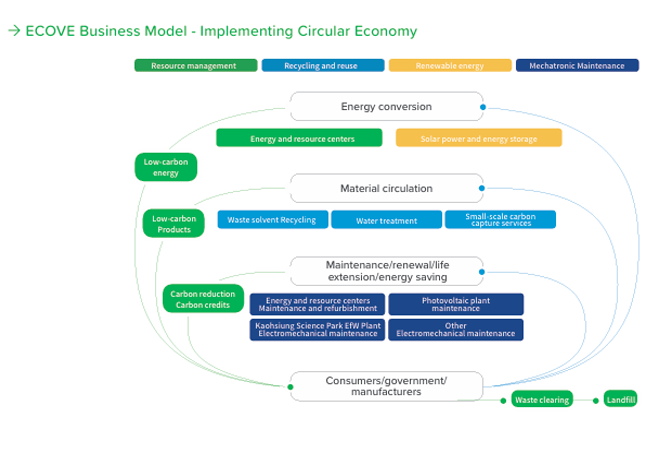
Under the goal of net zero emission by 2050, ECOVE has been committed to green investment and operation services in resource recycling and renewable energy. With a circular economy mindset and an environmentally friendly perspective, ECOVE has been actively cooperating with the government's policies on net zero carbon emission and the environment to provide low-pollution, low-emission, and high-energy-efficiency resource recycling and renewable energy, with a view to achieving a win situation for ECOVE, its partners, stakeholders, and the environment, and to do its utmost to safeguard the sustainability of the ecosystem and biodiversity. Since 2017, ECOVE has taken the lead in adopting the BS 8001 Circular Economy Guidelines, which aims to enhance economic, environmental and social benefits through optimal resource management, and to improve the recycling rate and Resource Cycling EfficiencyTM of every resource, so as to achieve the implementation of and compliance with the principles and models of the circular economy in the whole business area. Since2022, ECOVE has been conducting a comprehensive carbon inventory of its consolidated subsidiaries and obtaining external verification, as well as applying for carbon footprint certification for its waste incineration services, in order to provide lower carbon services. Currently, there are four plants that have obtained product carbon footprint certification: Keelung Plant, Miaoli Plant, Xizhou Plant, and Gangshan Plant.


The Taoyuan Biomass Energy Center officially commenced operations in 2024, as it is Taiwan's first new-generation incinerator, with an energy efficiency of up to 27%. Additionally, it features the largest anaerobic digestion power generation facility from food waste biogas in Taiwan. In total, ECOVE facilities processed 2,698,878 metric tons of waste through incineration throughout the year, generating 1,531,608 MWh of energy, resulting in a carbon reduction benefit of 780,900 metric tons of CO2e. The anaerobic treatment of food waste amounted to 15,632 metric tons, producing 1,656.2 MWh of energy-from-waste, with a carbon reduction benefit of 818.2 metric tons of CO2e. The recycling of waste solvents reached 14,913 metric tons, yielding 3,883 metric tons of products. The reclaimed water production reached 19.81 million metric tons, equivalent to the daily water consumption of 69.032 million people, while the total wastewater treatment in Taiwan was approximately 26.28 million metric tons. In terms of solar power, the annual electricity generation reached 121,546 MWh, with an annual carbon reduction benefit of approximately 60,000 metric tons, and the service electricity supplied amounted to 14,332 MWh, assisting industries in achieving a carbon reduction benefit of about 7,000 metric tons.